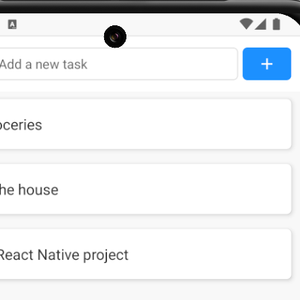
In my previous react native sqlite series, I've shown how you can use different storage providers for your app, and most importantly how you can integrate expo-sqlite, test it and make it work from the web.
Bad part about it is that SQLite on the web (SQL.js) won't be persisted between sessions. It is possible though. Requires a bit of work and the help of indexedDB.
Expo SQLite on the web
I've made it possible with SQL.js, expo platform specific modules and applying the adapter pattern. There's a post about it. Here's a partial snippet how it looks like, and check out the full code at github.
import { BindParams } from 'sql.js';
import initSqlJs from 'sql.js';
export type SQLiteDatabase = any;
const sqlPromise = initSqlJs({
locateFile: (file) => `https://sql.js.org/dist/${file}`,
});
export async function openDatabaseAsync(databaseName: string, options?: any): Promise<SQLiteDatabase> {
const SQL = await sqlPromise;
const db = new SQL.Database();
return {
execAsync: async (source: string): Promise<void> => {
db.exec(source);
},
runAsync: async (source: string, params: BindParams): Promise<any> => {
db.run(source, params);
return {
lastInsertRowId: db.exec('SELECT last_insert_rowid()')[0].values[0][0] as number,
changes: db.getRowsModified(),
};
},
};
}
What's for expo-sqlite is in the *.ts module, and the exact same interface is applied in the *.web.ts.
SQL.js doesn't persist between sessions
It operates in-memory by default, leading to data loss between sessions. And that's ok, there's a workaround for this. I use indexedDB for that.
My utility looks like:
import { openDB } from 'idb';
import { Database } from 'sql.js';
const DB_NAME = 'testmigrationsv1';
const STORE_NAME = 'databases';
const KEY_NAME = 'sqlite-data';
const idbPromise = openDB(DB_NAME, 1, {
upgrade(db) {
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains(STORE_NAME)) {
db.createObjectStore(STORE_NAME);
}
},
});
export async function loadFromIndexedDB(): Promise<Uint8Array | null> {
const idb = await idbPromise;
return await idb.get(STORE_NAME, KEY_NAME);
}
export async function saveToIndexedDB(db: Database) {
const dbData = db.export();
const idb = await idbPromise;
await idb.put(STORE_NAME, dbData, KEY_NAME);
}
Now, whenever an execAsync or runAsync is called, it also calls saveToIndexedDb.
And when I refresh, SQLite is created from IndexedDB binary data.
export async function openDatabaseAsync(databaseName: string, options?: any): Promise<SQLiteDatabase> {
const SQL = await sqlPromise;
const savedData = await loadFromIndexedDB();
const db = savedData ? new SQL.Database(savedData) : new SQL.Database();
return {
execAsync: async (source: string): Promise<void> => {
db.exec(source);
void saveToIndexedDB(db);
},
}
}I don't like the db.export to be called every single time when there's an insert, update or delete, but that's what I've come up with so far. There will be a performance hit once the database gets big. Also, I'm not sure if IndexedDB will hit a limitation once the binary export gets too big.
If a database has frequent writes, maybe wrapping saveToIndexedDb with debounce logic could help a bit.
So far, I've used this solution for a web version of my ListDuo app for tracking groceries.
GitHub for demo: https://github.com/amarjanica/react-native-sqlite-expo-demo